File Information
Library: Foundation
Package: Threading
Header: Poco/Condition.h
Description
A Condition is a synchronization object used to block a thread until a particular condition is met. A Condition object is always used in conjunction with a Mutex (or FastMutex) object.
Condition objects are similar to POSIX condition variables, which the difference that Condition is not subject to spurious wakeups.
Threads waiting on a Condition are resumed in FIFO order.
Member Summary
Member Functions: broadcast, dequeue, enqueue, signal, tryWait, wait
Constructors
Condition
Condition();
Creates the Condition.
Destructor
~Condition
~Condition();
Destroys the Condition.
Member Functions
broadcast
void broadcast();
Signals the Condition and allows all waiting threads to continue their execution.
signal
void signal();
Signals the Condition and allows one waiting thread to continue execution.
tryWait 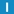
template < class Mtx > bool tryWait(
Mtx & mutex,
long milliseconds
);
Unlocks the mutex (which must be locked upon calling tryWait()) and waits for the given time until the Condition is signalled.
The given mutex will be locked again upon leaving the function, even in case of an exception.
Returns true if the Condition has been signalled within the given time interval, otherwise false.
wait 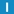
template < class Mtx > void wait(
Mtx & mutex
);
Unlocks the mutex (which must be locked upon calling wait()) and waits until the Condition is signalled.
The given mutex will be locked again upon leaving the function, even in case of an exception.
wait 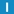
template < class Mtx > void wait(
Mtx & mutex,
long milliseconds
);
Unlocks the mutex (which must be locked upon calling wait()) and waits for the given time until the Condition is signalled.
The given mutex will be locked again upon successfully leaving the function, even in case of an exception.
Throws a TimeoutException if the Condition is not signalled within the given time interval.
dequeue 
void dequeue();
dequeue 
void dequeue(
Event & event
);
enqueue 
void enqueue(
Event & event
);